The shipping industry has been shifting towards decarbonisation and aiming for net zero carbon emissions by 2050. The transition requires ships to pursue superior energy efficiency and optimised operational functionality in a reliable, safe and economical way while reducing the environmental footprint.
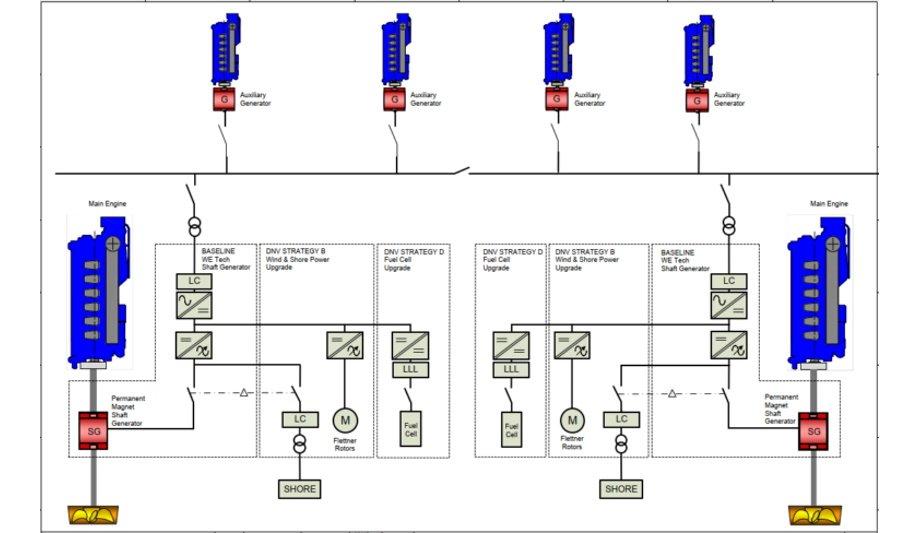
DNV’s latest study has presented several potential decarbonisation strategies (A-D) for a new LNG carrier design to determine feasible approaches, so as to achieve compliance with the IMO decarbonisation trajectory towards target 2050.
DNV’s vessel design study
In the DNV’s vessel design study, the shaft generator solution is listed as part of the baseline solution for the vessel, providing benefits of reducing carbon footprint and enabling operational flexibility.
WE Tech’s permanent magnet shaft generator with DC-link power distribution extends the possibilities of the shaft generator solution to new levels. Ship owners can expect a future-proof vessel beyond the baseline with superior energy efficiency to further reduce GHG emissions.
Permanent magnet shaft generators
It is nowadays essential to reduce GHG emissions through new technologies and low/zero carbon fuel
Martin Andtfolk, the Sales Manager of WE Tech Solutions, said “It is nowadays essential to reduce GHG emissions through new technologies and low/zero carbon fuel, to improve the environmental impact of vessels and to meet upcoming IMO regulations. The most effective way to achieve this target is to use permanent magnet shaft generators for power generation.”
Martin Andtfolk adds, “WE Tech’s permanent magnet shaft generator is compact-size with the highest efficiency over the full speed and power range. This solution has been applied to more than 100 vessels since 2010 and the market demand for it is constantly increasing. The reason behind this is that our solutions help ship-owners/operators to meet the IMO regulations for the Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII), which will go into effect already in 2023.”
Potential decarbonisation strategies A–D
The potential decarbonisation strategies A–D suggested by DNV are incorporated with five additional measures to reduce carbon intensity:
- Strategy A: Baseline technologies
- Strategy B: Wind and Shore Power
- Strategy C: Retrofit of onboard Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- Strategy D: Retrofit of Fuel Cells
DC-link power distribution
The DC-link power distribution enables the extension with shore power and fuel cell in a modular scaleable design to meet the energy requirements of the vessel. Instead of using auxiliary generators, the vessel can connect to shore power while in port which can reduce fuel consumption and CO2 emissions by an estimated 8-9% (relative to total annual emissions), according to DNV’s study.
By utilising the fuel cells, the fuel savings are estimated to be 6-7% fuel savings and the CO2 abatement potential in the same range.